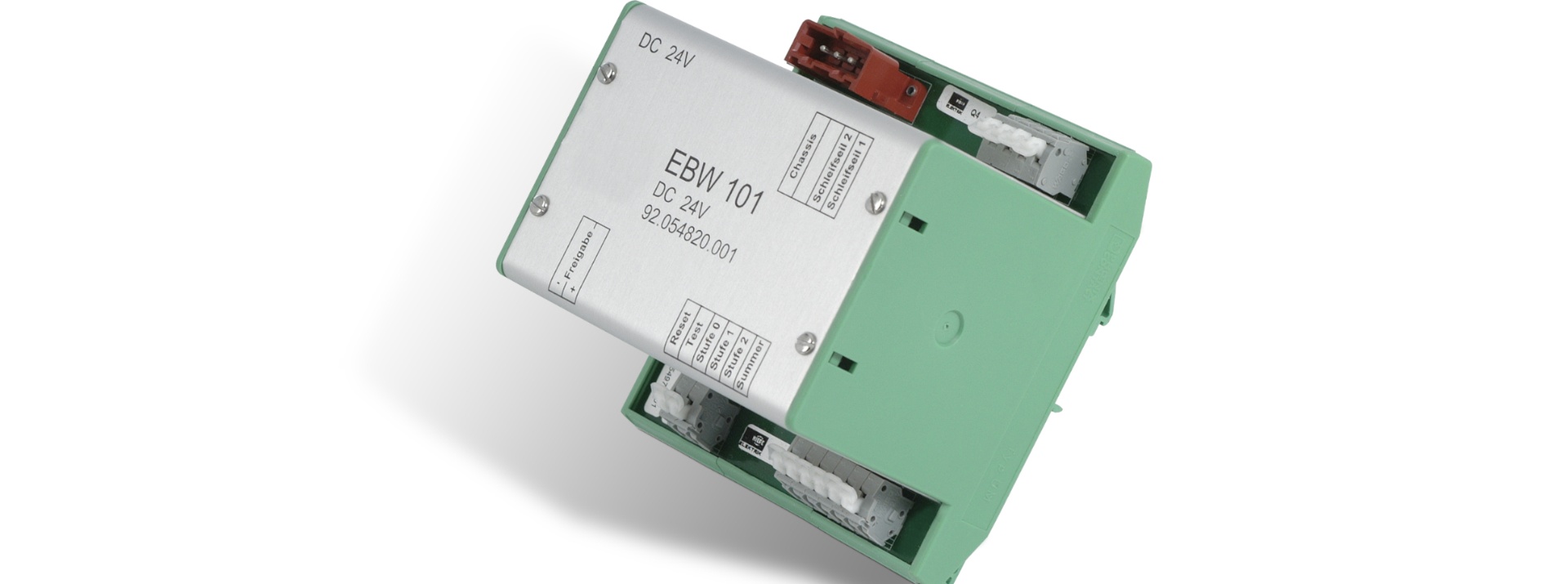
ELECTRONIC TOUCH VOLTAGE MONITOR KIEPE EBW 201
The Kiepe EBW 201 Touch Voltage Monitor is designed for usage in trolleybuses. It functionally replaces the previous “EIW Electronic Insulation Monitor”.
Trolleybuses are built using a “double insulation” safety precaution. The effectiveness of the insulation distances is examined egularly by measurement during maintenance intervals. Undiscovered pre-existing damages or the effects of moisture can worsen the condition of the insulation both short-term and / or temporarily when in use during passenger operation, and are difficult or impossible to detect by measurement during maintenance in the depot. Here, the Kiepe EBW 201 Touch Voltage Monitor offers the advantage of additional permanent monitoring supplementary to the stipulated insulation testing during passenger operation.
The method of measurement used for the Kiepe EBW 201 does not bridge any operational insulation distances. The small amount of cabling required makes the Kiepe EBW 201 especially suitable for the subsequent installation in vehicles which are already available.
Description
The Kiepe EBW 201 monitors the voltage between the vehicle chassis and the street surface. Passengers canbridge this voltage (touch voltage) especially when entering/leaving, (see Figure 1). Should the fault voltage between street surface and vehicle chassis reach certain specific (yet harmless) values, this is announced to the driver both acoustically as well as optically. The driver can then take the necessary measures for the passengers’ safety. Additionally, a possibility of automatic intervention for the separationof the overhead lines is provided. The touch voltage detection system consists of the Kiepe EBW 201 Electronic Touch Voltage Monitor, the driver’s controls and the 2 collector cables which are insulated and attached to the chassis. One collector cable establishes the contact between road surface and the Kiepe EBW 201 input. The second collector cable is used for the testing of the system and for the improvement of the contact to the road surface during operation.
More components